What are Shipping Rebates?

Shipping costs can be a significant expense for both consumers and businesses. To help offset these expenses, many companies offer shipping rebates—a system that provides refunds, store credits, or discounts on future purchases in exchange for meeting specific criteria. These rebates can make online shopping more affordable for consumers while helping businesses attract and retain customers.
For businesses, shipping rebates serve as an incentive tool, rewarding loyal customers and strategic partners for bulk purchases or consistent transactions. However, navigating these rebate programs can sometimes be complex, requiring a clear understanding of eligibility requirements, submission processes, and legal regulations.
In this blog, we’ll explore the different types of shipping rebates, how they work for both consumers and businesses, their benefits, challenges, legal considerations, and best practices for maximizing their advantages.
Table of Contents:
- What are Shipping Rebates?
- Different Forms of Shipping Rebates
- Types of Shipping Rebates
- How Shipping Rebates Work?
- Benefits of Shipping Rebates
- Challenges and Considerations of Shipping Rebates
- Legal and Ethical Aspects of Shipping Rebates
- Best Practices for Shipping Rebates
Jump to a section that interests you, or keep reading.
What are Shipping Rebates?
A shipping rebate is a refund or reimbursement offered to customers for a portion of the shipping costs incurred during the delivery of goods. The primary purposes of shipping rebates include:
-
Encouraging Purchases: By offering a rebate on shipping costs, businesses can make their products more appealing, especially to price-sensitive customers who might be deterred by high shipping fees.
-
Rewarding Customer Loyalty: Shipping rebates can serve as a reward mechanism for repeat customers, fostering long-term relationships and increasing customer retention.
-
Enhancing Customer Satisfaction: By reducing the effective shipping costs, customers perceive greater value in their purchases, leading to improved satisfaction and a higher likelihood of repeat business.
Different Forms of Shipping Rebates

Shipping rebates can be structured in various forms, each tailored to meet specific business objectives and customer preferences. The most common forms include:
-
Cash Refunds: In this model, customers receive a direct monetary reimbursement for a portion of their shipping expenses after completing the necessary rebate claim process. For instance, a customer might pay for shipping at the time of purchase and later submit a claim to receive a predetermined amount back. This approach provides immediate financial relief and is straightforward for customers to understand and utilize.
-
Store Credits: Instead of a cash refund, customers are granted store credits equivalent to the rebate amount. These credits can be applied to future purchases, encouraging repeat business and fostering customer loyalty. For example, a retailer might offer a $10 store credit for shipping costs incurred, which the customer can use on their next purchase.
-
Discounts on Future Purchases: Some businesses offer shipping rebates in the form of discounts on subsequent transactions. After paying for shipping on an initial order, the customer might receive a coupon or discount code applicable to future purchases, effectively reducing the overall cost of shopping with that retailer. This strategy not only compensates for shipping expenses but also incentivizes customers to return for additional purchases.
Types of Shipping Rebates
Shipping rebates are financial incentives designed to reduce or offset shipping costs for consumers and businesses. They are primarily categorized into two types: Consumer Shipping Rebates and Business-to-Business (B2B) Shipping Rebates.
Consumer Shipping Rebates
Retailers often provide shipping rebates to make their products more appealing by mitigating the additional expense of shipping. These rebates serve as a tool to attract price-sensitive customers and enhance overall satisfaction. The process typically involves customers paying the shipping fee upfront and then submitting a claim to receive a partial or full reimbursement.
Examples of Services Providing Shipping Rebates:
-
FreeShipping.com: This membership-based service offers consumers rebates on shipping fees incurred while shopping at over 1,000 affiliated retailers. Members can claim up to $10 per shipping rebate, with an annual cap of $500. The process involves submitting a rebate claim along with proof of purchase, and upon approval, the rebate amount is credited to the member's account.
-
ShipmentsFree: Similar to FreeShipping.com, ShipmentsFree provides members with the opportunity to claim up to $100 in shipping and return shipping rebates each month. Members submit their claims with the necessary documentation, and once approved, receive reimbursement for their shipping expenses.
Business-to-Business (B2B) Shipping Rebates
In the B2B sector, shipping rebates are employed as strategic tools to incentivize distributors and partners. These rebates are often structured around factors such as purchase volume, loyalty, and operational efficiency. By offering shipping rebates, suppliers encourage distributors to increase order quantities, maintain consistent purchasing patterns, and optimize their logistics operations.
Overview of the Ship and Debit Process:
A prevalent mechanism in B2B shipping rebates is the "Ship and Debit" process. This arrangement allows distributors to adjust pricing for end customers in response to market conditions without compromising their profit margins. The process involves several key steps:
-
Agreement Setup: The distributor and supplier establish terms for the ship and debit arrangement, specifying eligible products, approved price adjustments, rebate amounts, documentation requirements, and claim submission deadlines.
-
Request Submission: The distributor identifies a need to lower the selling price to compete effectively and submits a request to the supplier for approval of the price adjustment.
-
Approval: The supplier reviews the request and, if deemed appropriate, approves the price adjustment, formalizing the agreement.
-
Product Shipment and Sale: The distributor sells the product to the end customer at the reduced price, adhering to the terms of the approved agreement.
-
Claim Submission: After the sale, the distributor submits a claim to the supplier for the difference between the standard price and the discounted price offered to the end customer. This claim includes all necessary documentation to substantiate the transaction.
-
Reimbursement: Upon verification of the claim, the supplier reimburses the distributor for the approved amount, ensuring that the distributor's margins are protected despite the reduced selling price.
This process enables suppliers to maintain consistent pricing structures while allowing distributors the flexibility to respond to competitive market dynamics. Effective management of ship and debit agreements requires meticulous record-keeping and clear communication between all parties to ensure transparency and accuracy in claims and reimbursements.
How Shipping Rebates Work?
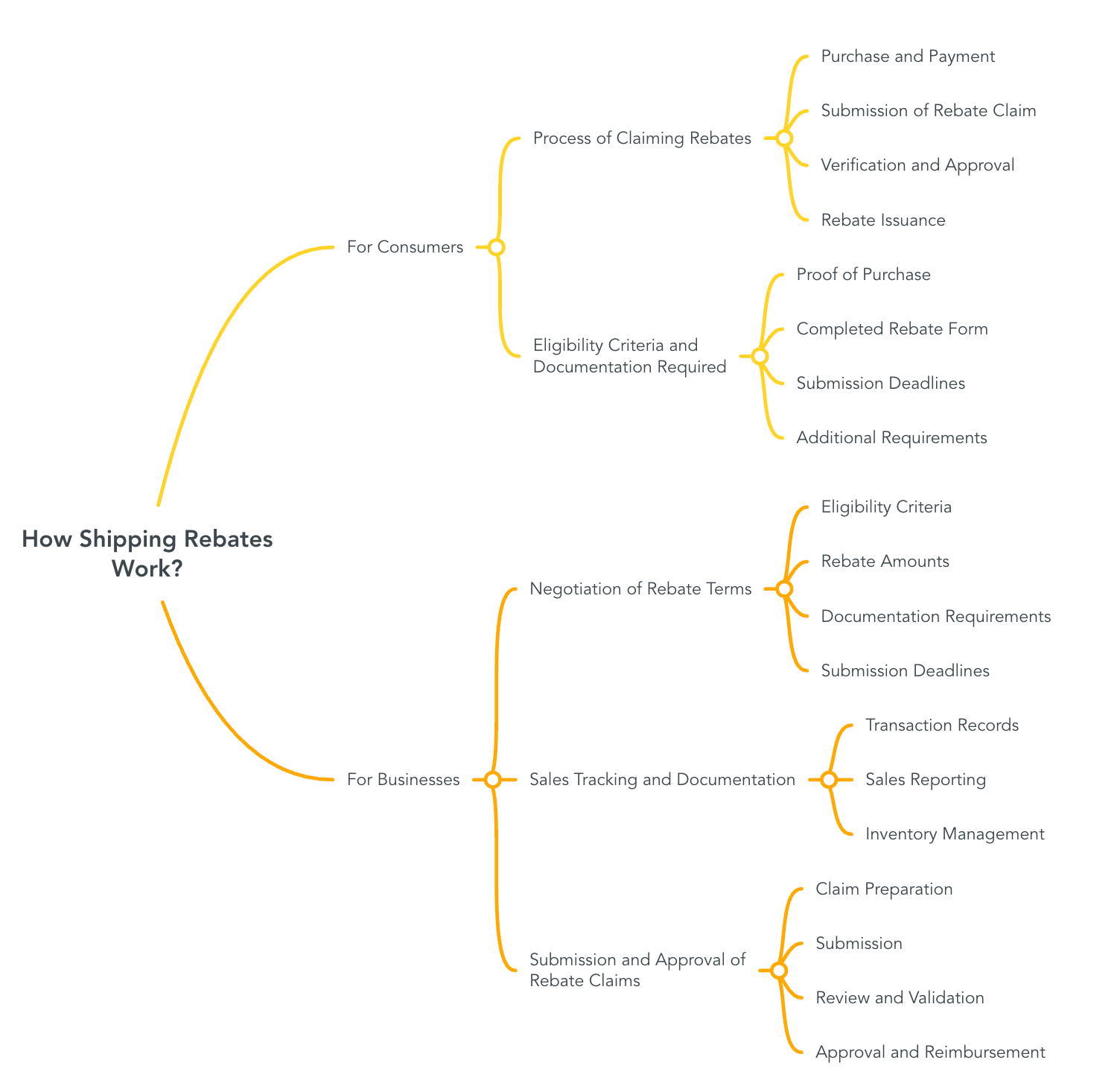
Shipping rebates are incentives offered to consumers and businesses to offset shipping costs, encouraging purchases and fostering loyalty. The processes for claiming and managing these rebates differ between consumers and businesses.
For Consumers:
Process of Claiming Rebates
-
Purchase and Payment: Consumers buy products and pay the full shipping cost at the time of purchase.
-
Submission of Rebate Claim: After the purchase, consumers submit a rebate claim through methods such as mail-in forms, online portals, or in-store submissions.
-
Verification and Approval: The issuing company verifies the submission against predefined criteria to validate the claim.
-
Rebate Issuance: Once approved, the rebate is processed, and consumers receive their reimbursement via checks, electronic transfers, or gift cards.
Eligibility Criteria and Documentation Required
-
Proof of Purchase: A valid sales receipt or invoice indicating the purchase date, item details, and shipping charges.
-
Completed Rebate Form: Accurately filled out with personal information and purchase details.
-
Submission Deadlines: Claims must be submitted within a specified timeframe, often within 30 days of purchase.
-
Additional Requirements: Some programs may require original packaging, barcodes, or online order confirmations.
Adhering to these criteria and providing the necessary documentation ensures a smoother rebate process.
For Businesses:
Negotiation of Rebate Terms
In B2B contexts, shipping rebates are often part of negotiated agreements between suppliers and distributors. Key aspects include:
-
Eligibility Criteria: Defining which products and transactions qualify for rebates.
-
Rebate Amounts: Agreeing on the rebate value based on factors like purchase volume or customer segments.
-
Documentation Requirements: Specifying necessary records for claim validation.
-
Submission Deadlines: Establishing timelines for claim submissions.
Clear agreements prevent misunderstandings and facilitate efficient rebate management.
Sales Tracking and Documentation
Accurate tracking and documentation are crucial for businesses to manage shipping rebates effectively:
-
Transaction Records: Maintain detailed records of purchases, sales, and shipping costs.
-
Sales Reporting: Regularly report sales data to suppliers, detailing quantities sold, pricing, and customer information.
-
Inventory Management: Track inventory levels to correlate sales data with stock movements.
Robust documentation supports accurate rebate claims and minimizes disputes.
Submission and Approval of Rebate Claims
The process for businesses to claim shipping rebates involves:
-
Claim Preparation: Compile necessary documentation, including sales invoices, proof of shipment, and any required forms.
-
Submission: Submit the claim to the supplier within the agreed timeframe, ensuring all information is accurate and complete.
-
Review and Validation: The supplier reviews the claim, verifying the provided data against the agreement terms.
-
Approval and Reimbursement: Once validated, the supplier approves the claim and issues the rebate, often as a credit note or direct payment.
Benefits of Shipping Rebates
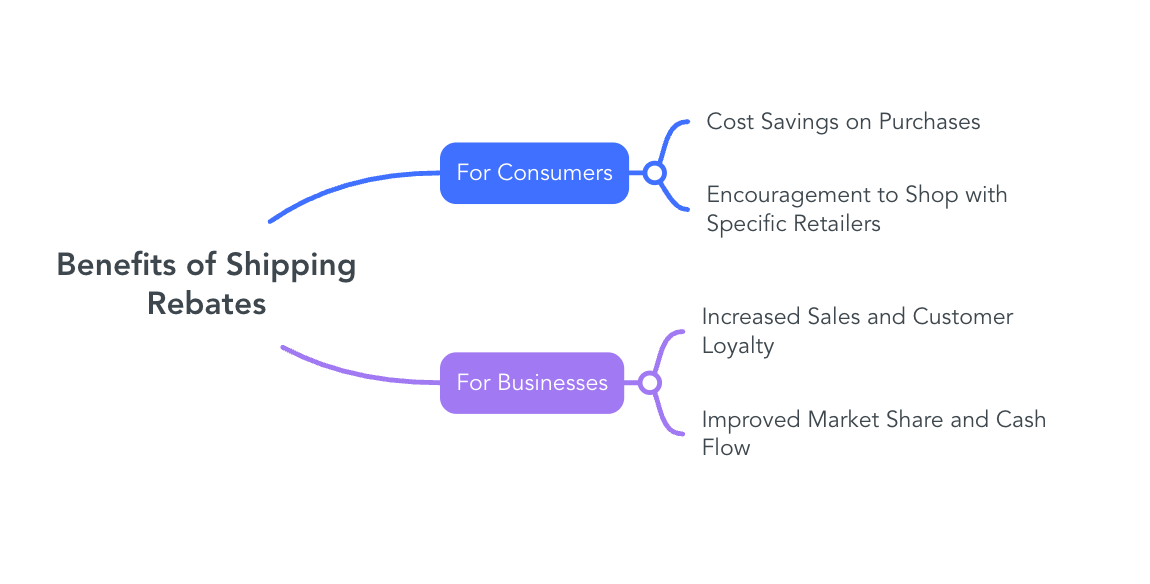
Shipping rebates offer distinct advantages to both consumers and businesses by mitigating shipping costs and fostering favorable purchasing behaviors.
For Consumers:
-
Cost Savings on Purchases: Shipping rebates provide consumers with partial or full reimbursement of shipping expenses, effectively reducing the overall cost of their purchases. This financial relief can make products more affordable and appealing, especially for price-sensitive shoppers. Studies have shown that rebates make consumers 75% more likely to make a purchase, far exceeding promotions like contests or sweepstakes.
-
Encouragement to Shop with Specific Retailers: Retailers that offer shipping rebates can differentiate themselves in a competitive market. By alleviating shipping costs, these retailers enhance the perceived value of their offerings, encouraging consumers to choose their services over competitors who do not provide such incentives. This strategy not only attracts new customers but also fosters repeat business, as shoppers are more likely to return to retailers that help them save on shipping expenses.
For Businesses:
-
Increased Sales and Customer Loyalty: Implementing shipping rebate programs can lead to a significant boost in sales. By reducing the effective cost of purchases, businesses make their products more accessible, prompting consumers to buy more frequently. Additionally, customers who benefit from shipping rebates are more likely to develop loyalty to the brand, resulting in repeat purchases and long-term relationships. Rebate programs encourage repeat business by rewarding customers for making multiple purchases over time.
-
Improved Market Share and Cash Flow: Shipping rebates can serve as a strategic tool to capture a larger market share. By offering financial incentives that competitors may lack, businesses can attract a broader customer base. Moreover, increased sales volume generated through rebate programs can enhance cash flow, providing the necessary capital to invest in other areas of the business, such as product development or marketing initiatives.
Challenges and Considerations of Shipping Rebates
Shipping rebates present various challenges for both consumers and businesses. Understanding these issues is essential for effectively navigating and managing rebate programs.
For Consumers:
-
Understanding Eligibility and Submission Deadlines: Consumers often encounter difficulties in comprehending the specific eligibility criteria and submission deadlines associated with shipping rebates. Rebate programs may have intricate terms and conditions, including purchase requirements, deadlines for submission, and necessary documentation. Failure to adhere to these stipulations can result in denied claims, leading to frustration and missed savings opportunities. Clear communication from retailers about rebate terms and proactive consumer engagement in understanding these details are crucial to ensure successful rebate redemption.
-
Potential Complexities in the Rebate Process: The rebate redemption process can be cumbersome, involving multiple steps such as completing detailed forms, providing proof of purchase, and adhering to strict submission guidelines. These complexities can deter consumers from pursuing rebates, leading to low redemption rates. Moreover, delays in processing and receiving rebates can diminish the perceived value of the offer. Simplifying the rebate process and providing clear instructions can enhance consumer participation and satisfaction.
For Businesses:
-
Administrative Complexities in Managing Rebate Programs: For businesses, administering shipping rebate programs involves significant logistical efforts. Managing multiple rebate agreements, each with distinct terms and conditions, can lead to increased complexity and potential errors. Manual processes for tracking and processing rebates are prone to inefficiencies and inaccuracies. Implementing automated rebate management systems can streamline operations, reduce administrative burdens, and improve accuracy.
-
Potential for Disputes and the Need for Accurate Documentation: Accurate documentation is vital to prevent disputes between businesses and their partners or customers regarding rebate eligibility and amounts. Misunderstandings or miscommunications about rebate terms can lead to conflicts, affecting business relationships and financial outcomes. Maintaining meticulous records and ensuring transparent communication about rebate agreements can mitigate these risks. Regular audits and clear documentation practices are essential to uphold the integrity of rebate programs.
Legal and Ethical Aspects of Shipping Rebates
Shipping rebates, while beneficial in offsetting transportation costs, are subject to various legal and ethical considerations. Understanding the regulatory landscape, historical legal precedents, and the importance of compliance is essential for businesses and consumers engaged in these practices.
Overview of Regulations Governing Shipping Rebates
In the United States, the regulation of shipping rebates is primarily governed by federal laws aimed at ensuring fair competition and preventing discriminatory practices in the transportation industry. The Shipping Act of 1984, administered by the Federal Maritime Commission (FMC), prohibits carriers from offering deferred rebates and engaging in unjustly discriminatory practices. Specifically, the Act states that carriers may not "offer or pay any deferred rebates" and must avoid giving "any undue or unreasonable preference or advantage" in their services.
Additionally, 49 U.S. Code § 14902 imposes civil penalties on individuals or entities that accept rebates from carriers, holding them liable for three times the amount received as a rebate.
Historical Context and Legal Cases Related to Shipping Rebates
Historically, shipping rebates have been a contentious issue, leading to significant legal actions. The Elkins Act of 1903 was a pivotal U.S. federal law that amended the Interstate Commerce Act of 1887. It authorized the Interstate Commerce Commission (ICC) to impose heavy fines on railroads offering rebates and on shippers accepting them, aiming to eliminate discriminatory pricing practices.
In more recent times, the FMC has taken action against carriers for imposing unjust and unreasonable charges. For instance, in a case involving Evergreen Shipping Agency (America) Corp., the FMC charged the company for imposing unreasonable detention charges on a trucking company for the late return of a shipping container during periods when the port was closed and could not accept the return.
Importance of Compliance to Avoid Legal Issues
Compliance with shipping rebate regulations is crucial to avoid legal repercussions and maintain fair market practices. Violations can lead to substantial fines, legal disputes, and reputational damage. For example, a federal court imposed a $56,000 fine against a U.S. representative of a foreign exporter who refused to comply with rebate regulations.
Businesses must ensure that any rebate programs are transparent, non-discriminatory, and fully compliant with applicable laws. This includes maintaining accurate documentation, adhering to fair pricing practices, and avoiding preferential treatment that could harm competition. Consumers should also be aware of the legal frameworks governing shipping rebates to understand their rights and obligations.
Best Practices for Shipping Rebates
Shipping rebates can offer significant advantages to both consumers and businesses. To maximize these benefits, it's essential to follow best practices tailored to each group's unique needs and challenges.
For Consumers:
Tips for Successfully Claiming Shipping Rebates
-
Understand Eligibility Requirements:
- Carefully review the rebate's terms and conditions to ensure your purchase qualifies.
- Take note of any specific product models, purchase locations, or timeframes stipulated.
-
Adhere to Submission Guidelines:
- Complete all required forms accurately and legibly.
- Include necessary documentation, such as original receipts, UPC codes, or online order confirmations.
-
Meet Submission Deadlines:
- Submit your rebate request within the specified timeframe to avoid disqualification.
- Consider sending submissions via traceable mail or retaining proof of digital submission.
-
Keep Copies of All Documentation:
- Maintain records of submitted materials for future reference or in case of disputes.
- Organize documents systematically to track the status of multiple rebate claims.
Awareness of Potential Scams and How to Avoid Them
-
Verify Retailer and Rebate Authenticity:
- Ensure the rebate is offered by a reputable retailer or manufacturer.
- Be cautious of unsolicited rebate offers or those requiring upfront payments.
-
Protect Personal Information:
- Only provide necessary information on official rebate forms.
- Avoid sharing sensitive data, such as Social Security numbers, unless absolutely required and verified.
-
Monitor Rebate Processing:
- Track the progress of your rebate submission using any provided tools or contact points.
- Follow up promptly if the rebate is not received within the advertised timeframe.
For Businesses:
Strategies for Implementing and Managing Rebate Programs Effectively
-
Set Clear Goals and Objectives:
- Define what the rebate program aims to achieve, such as increasing sales volume, promoting new products, or enhancing customer loyalty.
- Ensure these goals align with broader business strategies.
-
Establish Transparent Terms and Conditions:
- Clearly outline eligibility criteria, submission procedures, and deadlines.
- Communicate these terms effectively to consumers to prevent misunderstandings.
-
Leverage Technology for Management:
- Implement automated systems to track rebate submissions, process claims, and manage data efficiently.
- Utilize analytics to monitor program performance and identify areas for improvement.
-
Regularly Review and Adjust the Program:
- Continuously assess the effectiveness of the rebate program against set objectives.
- Be prepared to make adjustments in response to market changes or consumer feedback.
Ensuring Transparency and Fairness in Rebate Offerings
-
Maintain Accurate Record-Keeping:
- Keep detailed records of all transactions, submissions, and communications related to the rebate program.
- This practice aids in resolving disputes and ensures compliance with regulatory requirements.
-
Communicate Openly with Consumers:
- Provide clear instructions and support channels for rebate submissions.
- Be transparent about processing times and any potential delays.
-
Ensure Compliance with Legal Standards:
- Stay informed about regulations governing rebate programs to avoid legal pitfalls.
- Implement measures to prevent fraudulent claims and protect consumer data.
Conclusion
Shipping rebates play a crucial role in reducing shipping expenses for consumers while helping businesses drive sales and maintain customer loyalty. When used effectively, they provide a win-win scenario—shoppers enjoy cost savings, and companies strengthen their competitive edge. However, both consumers and businesses must be aware of the complexities involved, from understanding eligibility and avoiding scams to ensuring compliance with legal regulations.
By following best practices—such as carefully reviewing rebate terms, tracking submissions, and maintaining transparency—consumers can make the most of shipping rebate opportunities, while businesses can implement rebate programs that are efficient, fair, and legally compliant. With a well-structured approach, shipping rebates can be a valuable tool in today’s online shopping and logistics environment.
