What is Rebate Processing?

Businesses ranging from manufacturers to retailers use rebate programs to incentivize purchases without directly impacting product pricing. But, the success of these programs depends on the efficiency and accuracy of the rebate processing itself.
From setting up complex agreements to validating claims and issuing timely payments, rebate processing ensures that all stakeholders reap all the benefits. This blog will explore the essentials of rebate processing, its workflow, best practices, and the technology that makes it more efficient.
Table of Contents:
- What is Rebate Processing?
- Rebate Processing Workflow
- Rebate Processing Vs Rebate Management
- Challenges in Rebate Processing
- Best Practices for Rebate Processing
- Conclusion
Jump to a section that interests you, or keep reading.
What is Rebate Processing?
Rebate processing is a set of procedures used to execute a rebate program to ensure promotional offers are fulfilled, and incentives are provided to both vendors and customers.
Rebate Processing Workflow
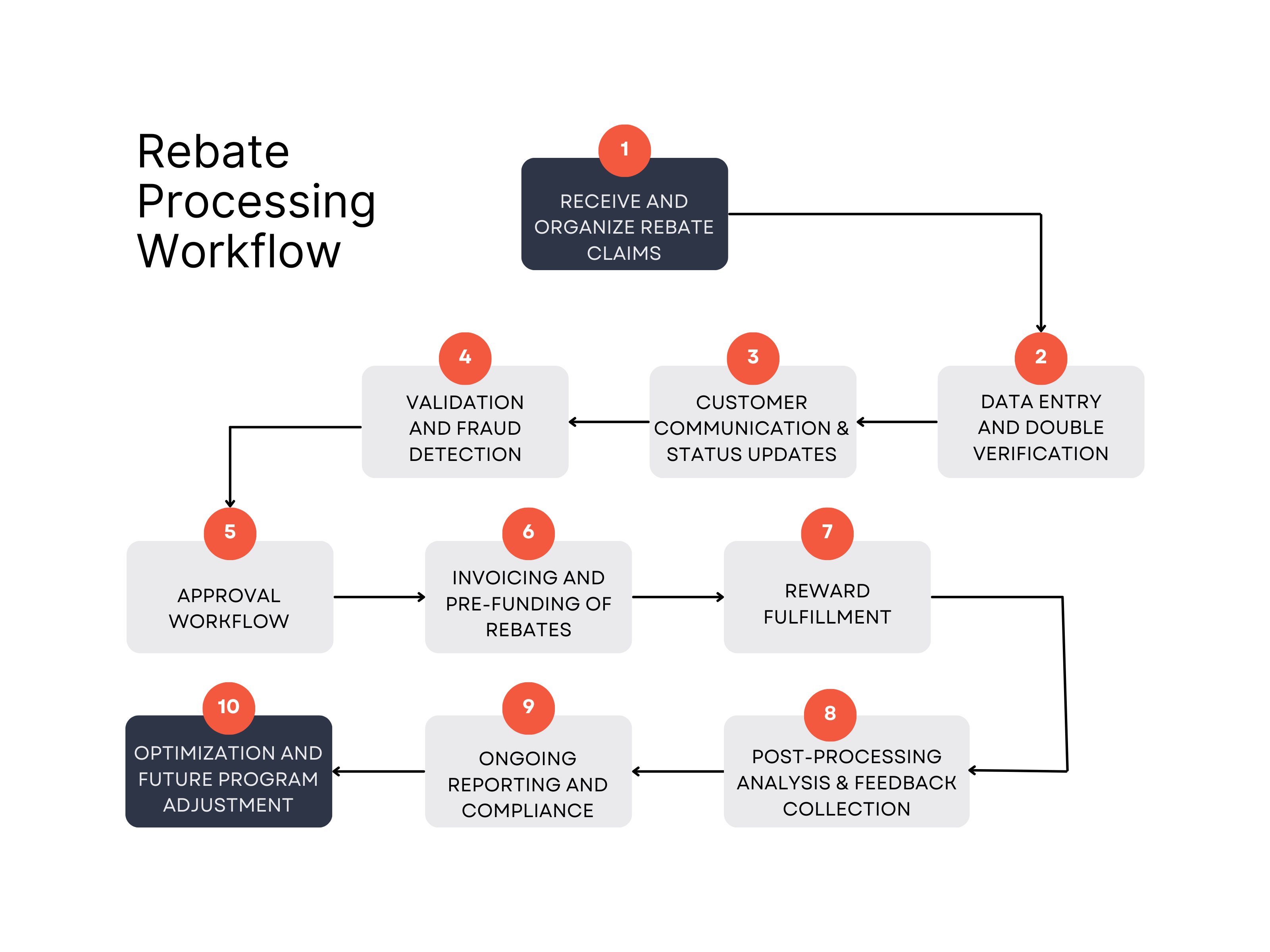
Receive and Organize Rebate Claims
Claims can be received via mail, online portals, apps, or even text messages. Choose methods based on customer convenience and your business capabilities. Many companies now favor digital submission.
Sort submissions by campaign type or promotional offer, as multiple rebate campaigns might be running simultaneously. This categorization is important for accurate tracking and reporting.
Ideally, aim to scan or log all submissions into the system within 24–36 hours of receipt to keep the process moving efficiently.
Data Entry and Double Verification
Information from each submission (e.g., customer details, purchase information, claim specifics) is entered into the rebate management system. Automated OCR (Optical Character Recognition) can help extract data from physical or scanned forms to reduce manual entry.
To ensure accuracy, use a double-entry system where two operators independently enter data. Any discrepancies can be flagged and corrected. This step is important to minimize errors, especially with large volumes of claims.
Customer Communication and Status Updates
Notify customers when their claim has been received. Regular updates on the claim’s status, such as when it enters the processing, approval, or payment phases, will reduce customer inquiries and build trust.
Maintain open channels for customer inquiries. Clear, proactive communication about expected processing times and claim status improves the customer experience and satisfaction.
Validation and Fraud Detection
Each claim is checked against the rebate program’s specific terms. Key checks include purchase date, product eligibility, quantity purchased, and purchase location. For instance, if a volume-based rebate requires a certain quantity, verify that this threshold has been met.
Use technology to detect potential fraud by checking for duplicate submissions, suspicious addresses, or altered documents. Many systems now cross-check with fraud databases and use pattern recognition to flag unusual or high-risk submissions.
Approval Workflow
Once a claim passes validation, it moves to approval. Some companies use automated workflows within their rebate management software to accelerate this process, especially for straightforward claims. However, complex claims may require manual review.
Every approved claim should be logged in detail within the system. This documentation is essential for auditing purposes and helps ensure transparency if any issues arise later.
Invoicing and Pre-Funding of Rebates
Avoid delays by setting up a pre-funded account dedicated to rebate payouts. This ensures funds are readily available, thus minimizing the time between approval and payout.
Generate invoices internally or request funds from rebate-specific budgets. Depending on the claim volume, consider weekly, biweekly, or monthly invoicing to simplify accounting and avoid cash flow interruptions.
Reward Fulfillment
Once funded, issue the reward to the customer. Rebates can be fulfilled in various formats, including:
- Physical Checks: Traditional but slow. Requires mailing and has higher processing costs.
- Electronic Transfers: Fast and convenient, usually deposited directly into customer accounts.
- Prepaid Rebate Cards: Branded cards, either virtual or physical, which can be used like a debit card.
- Digital Rewards: Instant virtual options like e-gift cards or direct account credits, preferred for speed.
Most rebate programs aim to complete fulfillment within two weeks of claim submission. Electronic options often allow faster fulfillment and improve customer satisfaction.
Post-Processing Analysis and Feedback Collection
Analyze rebate processing metrics such as claim volume, approval rates, and average processing times. Evaluate overall success to determine if program objectives (e.g., sales growth, customer engagement) are being met.
Use customer surveys or follow-ups to understand how the rebate programs met their expectations and whether the redemption process was smooth. This feedback helps improve future rebate program designs and processing workflows.
Ongoing Reporting and Compliance
Generate reports detailing processing outcomes, including total claims submitted, approved, denied, and average processing time per claim. Track redemptions against program targets. Maintain a complete audit trail with timestamps, claim details, validation outcomes, and approval records for financial compliance and to address any disputes or audits.
Ensure the processing system adheres to financial, legal, and data protection standards. Any deviations can compromise program legitimacy and lead to regulatory issues.
Optimization and Future Program Adjustment
Use processing data to find inefficiencies or bottlenecks. For instance, if manual validation slows down the process, increase automation usage.
Review rebate structures and modify thresholds, incentive levels, or payout types based on program performance and feedback.
Rebate Processing Vs Rebate Management
Scope and Purpose
Rebate Processing focuses specifically on the operational tasks required to execute each rebate transaction, from the moment a customer or trading partner submits a rebate to the point where the payment or incentive is issued. The process follows a structured, step-by-step workflow that includes claim submission, validation, approval, and reward distribution.
Rebate Management is a broader approach that oversees the entire lifecycle of rebate programs. This includes designing rebate strategies, establishing and documenting terms, setting goals, measuring rebate program performance, optimizing programs, and ensuring that the rebates align with larger business objectives (like sales growth, clearing out certain inventory, or customer retention). Management involves high-level decisions that determine rebate programs' design, objectives, and analysis to maximize their long-term value.
Operational vs. Strategic Focus
Rebate Processing is operational and transaction-focused. It ensures that each rebates are handled accurately and in compliance with established terms. Processing tasks are mainly concerned with executing and fulfilling rebate claims accurately, which include:
- Verification of rebate claims against set criteria.
- Validation to prevent fraud.
- Approval workflows and funding disbursement.
- Record-keeping and reporting of each claim’s status and outcome.
Rebate Management, on the other hand, is program-focused. It deals with the creation and ongoing refinement of rebate programs to meet high-level business goals, such as improving profit margins, building loyalty, and incentivizing specific buying behaviors. Key management responsibilities include:
- Designing rebate structures (e.g., volume-based, growth-based, value-based rebates).
- Setting objectives (e.g., increasing market share, moving inventory).
- Establishing performance metrics and KPIs to track the program’s rebate effectiveness.
- Periodic reviews and adjustments to ensure rebates remain aligned with market conditions.
System Integration and Technology Usage
Rebate Processing relies heavily on technology for operational efficiency. Automated Rebate Processing Systems (RPS) streamline tasks like data entry, claim validation, fraud detection, and fulfillment. The focus here is on minimizing errors, accelerating processing times, and handling large volumes of transactions with accuracy.
Rebate Management uses broader tools such as Rebate Management Platforms (RMPs) or modules within ERP systems. These platforms go beyond individual transaction handling to include functionalities like:
- Configurable rebate agreement templates, where terms can be updated and negotiated.
- Scenario planning and forecasting, which help estimate the potential impact of new rebate offers on sales.
- Analytics and reporting features that provide insights into customer behaviors and rebate performance.
- Integration with CRM and other systems to share rebate data across departments (e.g., finance, sales, and marketing).
Time Frame and Long-Term Objectives
Rebate Processing is immediate and transaction-oriented, with the aim to execute individual claims efficiently. Each transaction is processed based on the conditions and rules set by the rebate agreement, and success is measured by the speed, accuracy, and efficiency of processing each claim.
Rebate Management is long-term and cyclical, that includes the rebate program’s design, execution, review, and changes. It comprises of evaluating whether rebate structures align with market demands, revising goals, and adjusting incentives over time to better support sales objectives. Success in rebate management is measured through broader metrics like customer retention rates and increased sales volume.
Risk Mitigation vs. Optimization
Rebate Processing emphasizes risk mitigation by ensuring each rebate transaction meets specific criteria, which involves robust validation and fraud detection protocols. This prevents financial loss through erroneous or fraudulent claims and protects program profitability at the transaction level.
Rebate Management focuses on program optimization, using data gathered from past transactions and customer interactions to refine program structure and terms. Optimization includes strategies like adjusting rebate levels, modifying eligibility criteria, or adding new rebate types to better meet business goals.
Compliance and Reporting Differences
Rebate Processing maintains compliance with financial and legal standards by validating each claim in adherence to rebate terms to ensure accurate record-keeping and reporting for auditing purposes. Processing tasks are also subject to stringent data protection policies to safeguard customer information.
Rebate Management ensures compliance on a program level by aligning rebate structures with industry regulations, financial reporting standards, and broader organizational policies. Management tasks include establishing auditable rebate agreements, tracking aggregate program spending, and ensuring rebate programs remain within budgetary and regulatory constraints.
Challenges in Rebate Processing

Data Accuracy and Entry Errors
High volumes of claims increase the risk of data entry errors, especially if manual input is involved, leading to inaccuracies in rebate validation and processing.
Rebate claims include various data points (like product codes, purchase dates, quantities, and locations), which must be accurately recorded and cross-verified. Any discrepancy will result in incorrect payouts or delays.
Fraud Prevention
Rebate programs are susceptible to fraudulent claims, such as duplicate submissions or falsified purchase documents. Fraud detection requires robust systems to identify patterns, validate claim authenticity, and prevent financial losses.
Identifying fraud requires advanced detection algorithms and, in some cases, manual review, which can be resource-intensive.
Complexity of Validation Criteria
Rebate programs have varied eligibility criteria based on product types, purchase thresholds, time frames, and more. Validating each claim against specific terms requires thorough checks that become laborious without automation.
Managing different rebate types, like volume-based, value-based, and growth-based, is also challenging, as each requires a unique set of conditions to be met.
Timeliness and Processing Speed
Slow processing times, often due to bottlenecks in validation or funding, can lead to delayed rebate payments, which diminishes customer satisfaction.
Seasonal spikes or high-volume promotional periods can overwhelm the processing system, causing further delays and risking compliance with fulfillment timelines.
Integration with Existing Systems
Integrating rebate management systems with existing ERP and CRM systems is important for accurate data sharing, but achieving smooth integration can be technically challenging.
Ensuring that transaction data is consistently updated across systems to reflect real-time rebate tracking is also important but often difficult in complex organizational environments.
Managing High Volume and Scalability
Scaling up rebate processing to handle high volumes of claims without compromising accuracy and speed requires substantial infrastructure and automated systems.
Ensuring that systems can handle peak processing loads without performance issues or downtime is critical for smooth operations.
Compliance and Audit Requirements
Rebate processing must comply with various financial and data protection regulations, like GDPR for data privacy, which necessitates stringent record-keeping and reporting standards.
Maintaining an audit trail for each rebate claim, including details on validation steps, approvals, and payments, is crucial for compliance but becomes labor-intensive without proper automation.
Customer Communication and Support
Customers expect regular updates on their rebate claim status. Without clear communication channels, customers may experience frustration, leading to a negative brand perception.
Responding to customer inquiries about claim status or resolving disputes over denied claims requires a well-staffed support team, adding to operational costs.
Pre-Funding and Cash Flow Management
Without dedicated pre-funding for rebate payouts, delays in funding can halt or slow down payment processing, impacting customer satisfaction.
Accurately forecasting redemption rates is difficult, and unexpectedly high claim volumes can strain cash flow and rebate budgets.
Program Tracking and Performance Analysis
Effective KPI Tracking: Measuring rebate program success requires tracking KPIs such as redemption rates, processing times, and customer satisfaction. Without proper analytics, it’s challenging to gauge a program’s effectiveness accurately.
Analyzing rebate data for performance insights is essential for optimization but requires sophisticated analytics tools and expertise to interpret the data effectively.
Technology and System Limitations
Many businesses still rely on manual or semi-automated systems, which lack the scalability and functionality needed to handle modern rebate processing demands. Implementing or upgrading to advanced rebate management platforms is difficult for companies with legacy systems.
Best Practices for Rebate Processing
Automate Rebate Processing Tasks
Automation minimizes manual data entry, speeds up validation, and reduces the risk of errors. Rebate management platforms can handle data capture, claim tracking, validation, and payment processing. Some software also integrates with existing systems, ensuring seamless data sharing, providing a single truth source, and allowing for real-time rebate tracking.
Maintain Accurate and Standardized Data Entry
Use a double-entry system to ensure data accuracy, where two operators input the same data separately, flagging any discrepancies for review. If processing physical rebate forms, use Optical Character Recognition (OCR) to digitize data from scanned forms, reducing manual entry time and errors.
Implement Robust Validation and Fraud Detection
Clearly outline eligibility terms to simplify validation and ensure customers understand the requirements. Standardized eligibility checks also streamline processing.
Employ fraud detection tools that can cross-check claims against fraud databases, flag duplicates, and recognize suspicious patterns, such as repeat submissions from the same address.
Ensure Timely Communication with Customers
Send automated acknowledgments upon claim receipt to reassure customers their rebate is being processed.
Notify customers of each stage of their rebate claim, such as processing, approval, and payment. Clear communication builds trust and reduces inquiries.
Provide dedicated support for rebate inquiries. Quick responses to questions and dispute resolutions will improve the customer experience.
Set Up a Pre-Funding System for Rebates
Maintain a dedicated, pre-funded account for rebate payouts. Pre-funding avoids delays associated with internal invoicing and payment approval, enabling faster rebate fulfillment.
Review funding levels periodically to ensure the account has sufficient funds, particularly during high-redemption periods.
Optimize the Claim Submission Process
Allow customers to submit claims through various channels, such as online portals, apps, and mail, to accommodate diverse customer preferences.
Minimize the complexity of required documents, ensuring only essential information is needed for claim verification, which improves completion rates and speeds up processing.
Prioritize Transparent and Regular Reporting
Track metrics like processing time, approval rates, claim volumes, and redemption rates. Reports provide insights into rebate program effectiveness and help identify bottlenecks.
Keep a complete audit trail with timestamps, claim details, validation notes, and payment records for compliance and dispute resolution.
Establish Clear, Data-Driven KPIs
Measure success using KPIs such as rebate redemption rates, claim processing time, and customer satisfaction. KPIs help in assessing program health and areas needing improvement.
Adjust KPIs based on historical data and program objectives, helping the team focus on high-impact areas and improve efficiency.
Implement Security and Compliance Measures
Adhere to data protection standards, like GDPR, by ensuring that rebate claim data is securely stored and access is limited to authorized personnel only. Ensure rebate processing meets financial and industry standards, with robust documentation to meet audit requirements.
Regularly Review and Adjust Rebate Programs
Conduct regular evaluations to assess whether rebate programs are meeting goals (e.g., driving sales, clearing inventory, increasing loyalty). Adjust rebate terms or create targeted rebate offers based on seasonal trends, customer preferences, and competitive pressures.
Conclusion
Overcoming the complexities of rebate processing such as setting up agreements, validating claims, and issuing payments efficiently can be difficult without the right tools.
Rebate management software such as Speedy Labs helps by simplifying the entire lifecycle of rebate management—from agreement documentation to claim processing and financial accruals.
Get in touch today with us today to not just improve operational efficiency but also strengthen partnerships for long-term growth and profitability.
