Problems with Manual Rebate Management & Their Solution

A mere 1% error rate in manual rebate management has the ability to translate into billions of dollars in lost revenue each year. These errors can also damage trust with trading partners and disrupt cash flow.
This guide addresses these challenges associated with manual rebate management and solutions for transitioning to modern, automated systems.
Table of Contents:
- The Challenges of Manual Rebate Management
- The Solutions – Moving Toward Automated Rebate Management
- 4 Steps to Transition from Manual to Automated Rebate Management
Jump to a section that interests you, or keep reading.
The Challenges of Manual Rebate Management
1. Complexity of Rebate Agreements
Manual rebate management is often hindered by the intricate nature of rebate agreements, which include diverse contract structures tailored to various business goals. Common types of rebate agreements include volume incentives aimed at boosting order sizes, performance incentives tied to specific growth metrics, product mix incentives to promote new or high-margin products, channel incentives for targeted sales channels, and end-of-life incentives designed to clear aging inventory. The diversity of these structures adds layers of complexity, as each agreement has unique terms, conditions, and thresholds.
While rebate agreements are inherently complex, the day-to-day realities of managing them, such as inconsistencies, data fragmentation, and manual labor, add additional layers of difficulty.
Contracts often run into hundreds of pages, with critical clauses expressed differently depending on the counterparty. For example, a clause appearing on page 24 in one contract might be on page 78 in another. Additionally, these documents lack standard formatting, making manual review tedious and error-prone. The unstructured nature of these agreements forces rebate managers to sift through large volumes of information, which complicates efforts to extract actionable insights.
2. Error-Prone Manual Processes
Reliance on spreadsheets and email-based workflows is a hallmark of manual rebate management, but it introduces significant risks. Spreadsheets, while versatile, lack standardization. They are prone to errors during data entry, calculations, or updates. Without automation, each step in the process, from preparing claim documents to securing approvals, becomes a potential point of failure.
The risk factors associated with manual processes are numerous. Common issues include keying errors, miscalculations, duplicate entries, and missed claims. Such errors erode trust with trading partners and create administrative backlogs.
Financial impacts extend beyond individual mistakes. Globally, error rates in rebate management processes result in billions of dollars in lost revenue annually. Even a small error rate, such as 1% on a substantial rebate portfolio, can lead to significant financial leakage, which emphasizes the inadequacy of manual methods for handling complex agreements.
3. Lack of Timely and Accurate Data
Manual rebate management also struggles with data quality and accessibility. Contracts are poorly digitized, which complicates efforts to extract essential information using OCR or other scanning technologies. Data related to agreements, amendments, and claims are frequently scattered across multiple repositories such as SharePoint or shared drives, which makes it difficult to establish a single source of truth.
The consequences of these data issues are severe. Delayed updates prevent organizations from obtaining real-time insights into rebate performance, which is essential for timely decision-making. For instance, if claim calculations or performance metrics are eight weeks behind the actual data curve, businesses risk making outdated decisions that fail to capitalize on emerging opportunities.
Missed opportunities are another critical concern. A lack of visibility into the financial and operational impacts of rebate agreements means businesses cannot assess whether their rebate strategies are delivering the intended outcomes. This not only undermines potential revenue growth but also prevents businesses from building stronger relationships with trading partners through transparent and best rebate management practices.
4. Lack of Timely and Accurate Data
Manual rebate management processes are hindered by fragmented and inconsistent data. Poorly digitized contracts result in incomplete or inaccurate data extraction, especially when optical character recognition (OCR) tools struggle with low-quality PDFs. Additionally, important data is frequently dispersed across multiple repositories, including file shares like SharePoint or other storage systems, complicating efforts to consolidate information.
Delayed data updates are another issue. With rebate calculations and claims often lagging behind real-time events, businesses lose the ability to make timely and informed decisions. This lag disrupts the ability to assess rebate performance and negatively impacts cash flow management.
The lack of visibility into rebate performance exacerbates missed opportunities. Without accurate, up-to-date information, companies struggle to evaluate whether their rebate strategies are yielding intended outcomes, which leads to suboptimal decision-making and missed chances for optimization.
5. Inefficient Workflows
Manual processes are inherently inefficient and involve numerous steps that consume significant time and resources. Preparing claim documents, securing supplier approvals, and integrating finalized claims into finance systems are managed through email and spreadsheets, which create redundancies and bottlenecks. Each step requires meticulous attention and increases the risk of delays and errors.
Collaboration between different departments, including sales, procurement, and finance, is frequently limited. Manual workflows often operate in silos, which prevents cross-functional teams from sharing information. This disconnect reduces the overall efficiency of rebate management and complicates efforts to align strategies across departments.
6. Scale and Volume of Agreements
Managing thousands of rebate agreements and amendments manually is an overwhelming task, especially for medium and large organizations. Each agreement comes with unique terms and conditions and requires individualized attention that manual systems are ill-equipped to handle. As businesses grow and the volume of agreements expands, these processes become unsustainable.
Manual systems also lack scalability, which makes it challenging for organizations to keep pace with increasing workloads. Adding resources, such as hiring more personnel or allocating interns to manage agreements, is a temporary fix that fails to address the root of the issue. The inability to scale efficiently results in administrative strain and prevents businesses from capitalizing on growth opportunities.
7. Stakeholder Management Challenges
Manual rebate management fails to meet the high expectations of stakeholders who demand immediate, accurate information. Executives require real-time insights into specific agreements or financial outcomes, but manual systems cannot provide these answers promptly. This delay undermines the ability to make quick and strategic decisions.
Administrative burdens further complicate stakeholder management. Manual processes consume considerable time and resources but fail to deliver actionable insights. This inefficiency frustrates stakeholders, limits organizational agility, and erodes confidence in the rebate management system.
The Solutions – Moving Toward Automated Rebate Management
1. Use Automation
Transitioning from manual systems to automated rebate management platforms is a transformative step for businesses aiming to enhance efficiency and accuracy. Automation replaces labor-intensive processes with technology-driven systems that simplify workflows, reduce errors, and increase operational speed. Key features of automated rebate platforms include contract creation, real-time claim tracking, and direct integration with financial systems.
2. Automate Repetitive Tasks
Manual processes such as data entry, claim preparation, and approvals consume significant time and are prone to errors. Automation, by AI and machine learning, simplifies these tasks by eliminating the need for manual intervention. Automated systems process high volumes of claims, track statuses, handle calculations with unparalleled speed and accuracy, and reduce administrative strain.
Integration with ERP systems ensures a smooth transition from claim generation to invoicing and reconciliation. This direct connection minimizes delays and ensures that financial data remains consistent across platforms to improve both accuracy and efficiency in financial reporting.
3. Improving Stakeholder Relationships
Automated rebate systems provide precise calculations and real-time updates to build transparency with trading partners. This clarity minimizes disputes and ensures that all parties have access to the same information.
Transparent processes pave the way for stronger partnerships. By consistently meeting rebate commitments and maintaining clear communication, businesses can establish mutually beneficial agreements and improve collaboration over the long term.
4. Automation of Complex Contract Management
AI simplifies the management of intricate rebate agreements by automating the extraction and analysis of key contract data. Tasks that previously required hours of manual review, such as interpreting large contracts and managing amendments, are now completed in minutes with superior accuracy.
5. Scalability and Repeatability
AI-driven systems ensure consistent performance and can scale to accommodate growing business needs. As businesses expand, AI tools adapt to handle increasing workloads without compromising efficiency or accuracy and provide repeatable results that enhance reliability.
6. Financial and Operational Impacts
Automated workflows reduce errors and inefficiencies, which directly cuts costs associated with manual processes and administrative delays. Accurate claims management also eliminates the financial risk of overpayments and missed rebates.
Proactive rebate collection supported by real-time insights enables better financial planning and decision-making. Businesses can optimize their rebate strategies to ensure maximum returns and contribute to sustained revenue growth.
With manual tasks automated, teams can redirect their focus to strategic activities such as negotiating better agreements, analyzing market trends, and strengthening customer relationships. This shift not only increases productivity but also drives innovation and long-term growth.
4 Steps to Transition from Manual to Automated Rebate Management
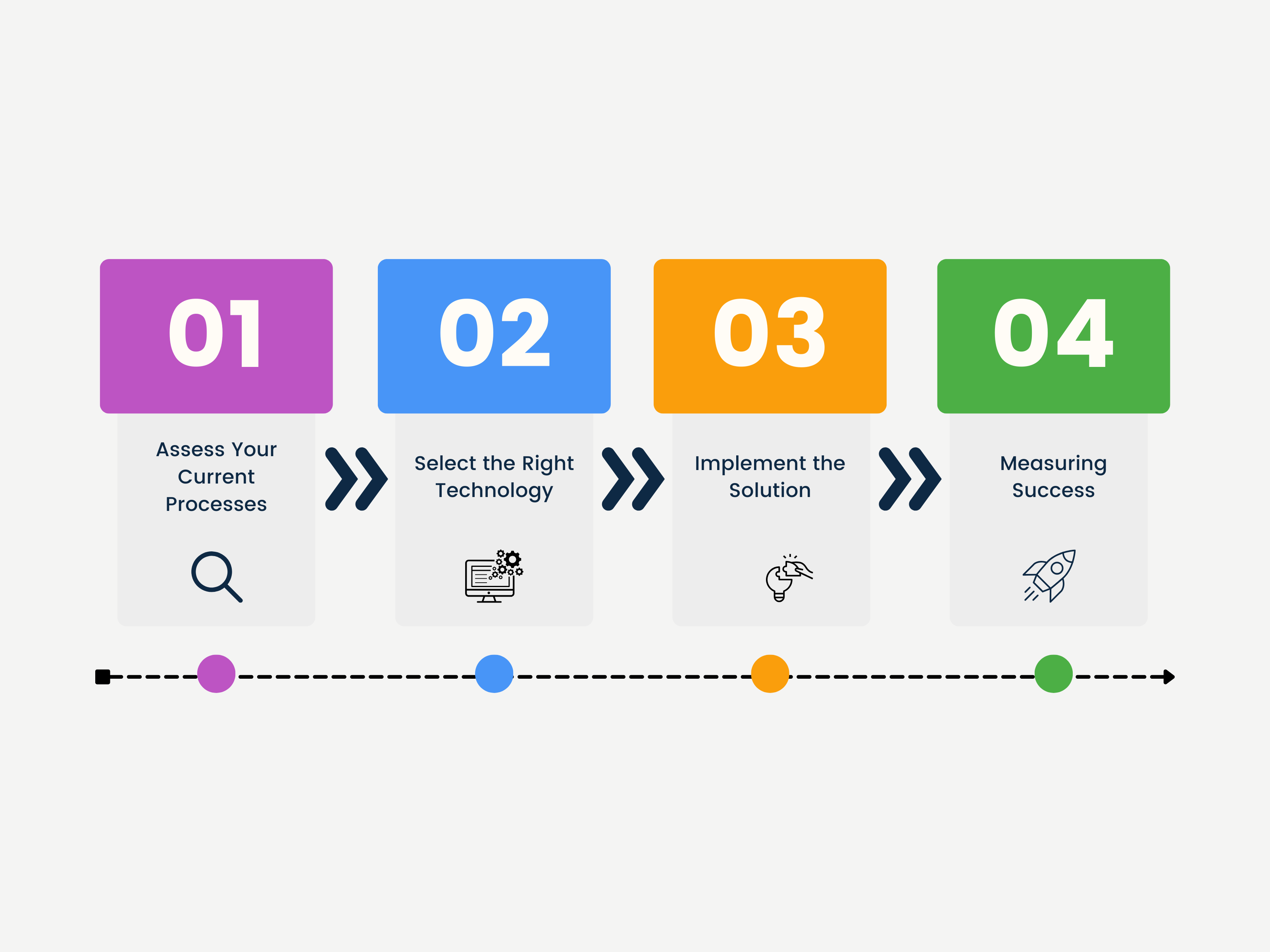
1. Assess Your Current Processes
The first step in transitioning to an automated rebate management system is to evaluate existing workflows and identify inefficiencies. Common bottlenecks include reliance on spreadsheets, repetitive manual tasks, and fragmented data storage. Analyzing these pain points helps to pinpoint areas where automation can provide the most significant impact.
Additionally, businesses should calculate the financial repercussions of current processes, such as the costs associated with errors, delayed claims, and administrative inefficiencies. For example, even a 1% error rate in manual rebate calculations can translate into substantial revenue losses annually, which underscores the urgency of implementing a more reliable system.
2. Select the Right Technology
Choosing the appropriate rebate management platform is important to ensure a successful transition. The ideal solution should offer features such as real-time analytics, centralized data management, ERP integration, and automated claim generation. Platforms like Speedy Labs have the ability to handle complex agreements, provide transparency, and improve operational efficiency.
When evaluating tools, businesses should also consider scalability, user-friendliness, and compatibility with existing systems. Selecting a platform that meets both current and future needs ensures long-term success.
3. Implement the Solution
A smooth implementation process is key to maximizing the benefits of automation. Begin by integrating the new system with existing tools such as ERP and accounting platforms for smooth data flow. Collaboration with IT and operations teams can help address technical challenges during the integration phase.
Training employees is equally important. Provide comprehensive training to ensure all users understand how to use the platform’s features. Clear communication about the benefits of automation helps gain stakeholder buy-in, which is crucial for driving adoption across the organization.
4. Measuring Success
Once the automated system is operational, track key performance indicators (KPIs) to measure its success. Metrics such as error rates, processing times, and ROI provide insights into the system’s impact. For example, reductions in claim discrepancies or faster rebate settlements can indicate significant improvements.
Conclusion
The risks of manual rebate management are too significant to ignore. Businesses must act now to modernize their rebate processes and tap into the potential of solutions like Speedy Labs. It automates rebate management by delivering both immediate results and sustainable success.
Schedule a demo with our team and take the first step toward optimized rebate management by exploring automated solutions tailored to your industry’s needs.
