The Complete Guide to Partnership Incentives

Partner incentives play an important role in building strong, productive collaborations between businesses and their partners. A well-structured incentive program not only drives sales but also encourages engagement, strengthens brand loyalty, and ensures long-term commitment.
While traditional commission-based rewards remain common, evolving industry trends highlight the need for a more strategic approach. Companies must align incentives with partner goals, balance financial and non-financial rewards, and leverage technology to optimize performance. This guide explores the different types of partner incentives, how to design an effective program, common challenges, and future trends shaping the partnership environment.
Table of Contents:
- What Are Partnership Incentives?
- How Incentives Drive Collaboration, Sales, and Retention?
- The Difference Between Financial and Non-Financial Incentives
- The Role of Incentives in Strengthening Partner Relationships
- Types of Partner Incentives
- Building an Effective Partner Incentive Program
- Common Challenges and How to Overcome Them
- Technology & Tools for Managing Partner Incentives
- Future Trends in Partner Incentives
Jump to a section that interests you, or keep reading.
What Are Partnership Incentives?
Partnership incentives are rewards, rebates, or benefits provided to business partners to encourage behaviors that align with company goals. These incentives motivate partners to increase sales, promote products, and participate in joint marketing initiatives. They can be structured as financial rewards, such as commissions and rebates, or non-financial benefits, like exclusive training and public recognition. The effectiveness of an incentive depends on how well it meets the needs of both the company and its partners.
How Incentives Drive Collaboration, Sales, and Retention?
Incentives encourage partners to actively engage with a business by offering tangible rewards for their efforts. Sales incentives, such as commissions and volume-based rebates, motivate partners to increase their purchase commitments. Promotional incentives help align sales and marketing efforts, creating joint campaigns that maximize market impact. Retention-focused incentives, including loyalty rebates and long-term service contracts, strengthen relationships by rewarding consistent engagement. Cost contribution rebates and special pricing agreements further enhance collaboration by sharing financial benefits and mitigating risks associated with fluctuating demand. By strategically designing incentives, businesses can ensure mutual value, resulting in sustained sales growth and long-term partnerships.
The Difference Between Financial and Non-Financial Incentives
Financial incentives provide direct monetary benefits, including commissions, rebates, discounts, and bonuses. They are commonly used to drive immediate sales and ensure partners remain competitive in the market. Volume-based rebates and MDFs fall under this category, offering structured rewards for meeting performance targets.
Non-financial incentives focus on added value beyond direct financial compensation. These include deal registration protection, co-marketing support, lead sharing, early product access, and advisory council participation. Partners may also receive training, exclusive event invitations, or public recognition. These incentives foster deeper engagement and loyalty by providing resources and opportunities that help partners succeed in the long term.
The Role of Incentives in Strengthening Partner Relationships
Strategic incentives transform transactional partnerships into collaborative relationships. By aligning incentives with shared objectives, businesses create a framework for joint success. Market development funds, co-branded marketing campaigns, and joint promotional activities enhance brand visibility and market reach. Stocking incentives and cost-sharing initiatives improve operational efficiency, ensuring mutual benefits in supply chain management. Recognizing partners through awards, exclusive events, and advisory roles builds goodwill and encourages continued collaboration. When incentives are structured thoughtfully, they create a sustainable ecosystem where both businesses and partners grow together.
Types of Partner Incentives
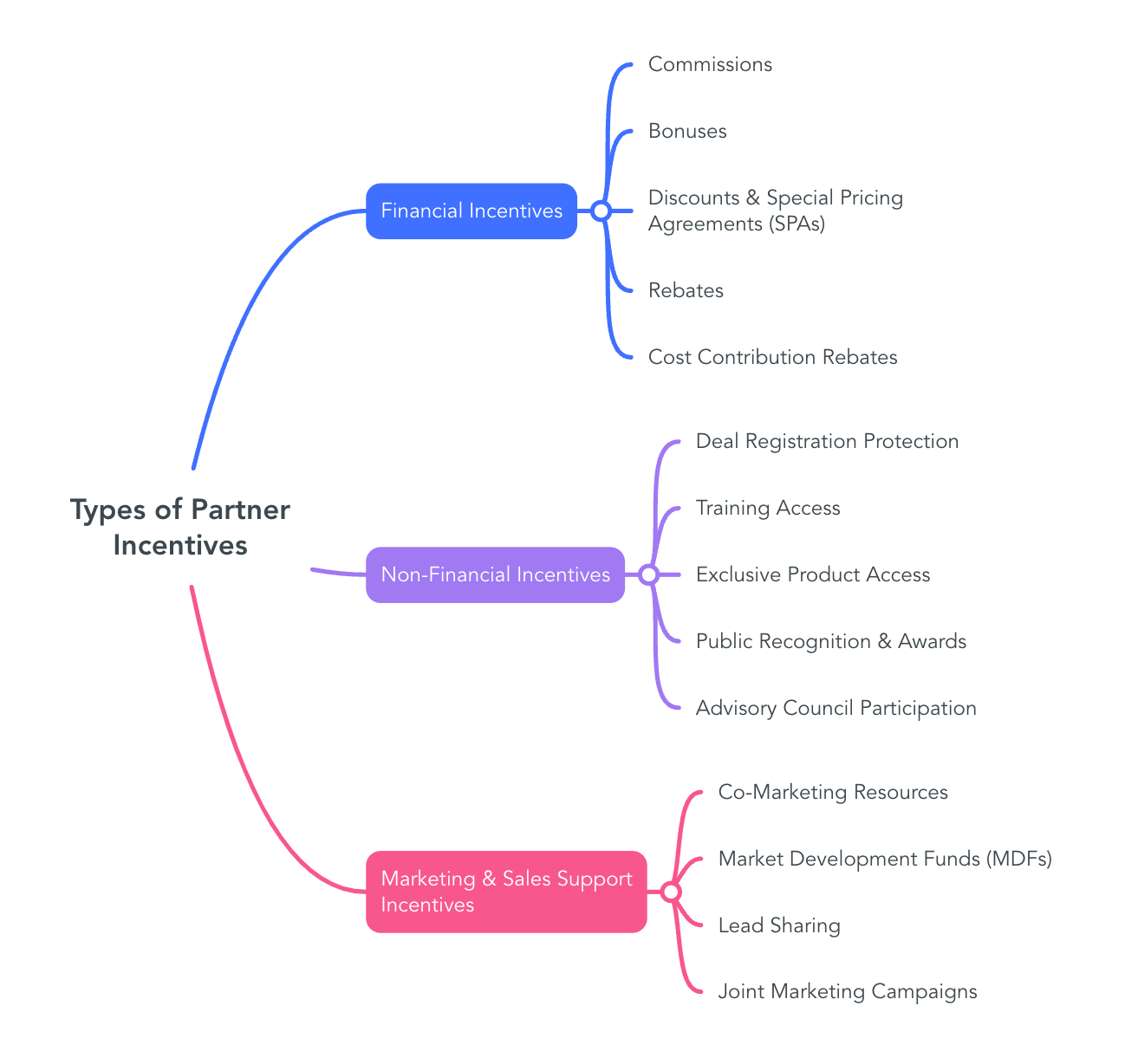
Financial Incentives
- Commissions: Commissions are one of the most commonly used financial incentives, offering a percentage-based reward for every sale a partner generates. While widely adopted, their impact varies—many partners see commissions as a supplementary benefit rather than a primary motivator.
- Bonuses: Bonuses provide extra financial rewards for partners who exceed specific sales milestones. Unlike standard commissions, these incentives are structured to drive peak performance, encouraging partners to push beyond their usual targets.
- Discounts & Special Pricing Agreements (SPAs): Discounts and SPAs give partners access to reduced pricing on select products or SKUs, helping them remain competitive in volatile markets. These agreements allow businesses to work collaboratively with partners to determine which products should be discounted based on demand and strategic objectives.
- Rebates: Rebates reward partners for reaching volume-based or long-term sales commitments. Volume rebates encourage larger purchases by offering incremental rewards, while loyalty-driven rebates ensure consistent engagement over time. Both strategies not only drive sales but also reinforce strong business relationships by aligning incentives with shared growth objectives.
- Cost Contribution Rebates: Cost contribution rebates help offset business expenses incurred by partners, such as marketing investments, infrastructure costs, or technology upgrades. Instead of being simple reimbursement mechanisms, they create opportunities for collaborative cost-sharing initiatives that drive efficiency and reduce financial strain for both parties.
Non-Financial Incentives
- Deal Registration Protection: Deal registration protection safeguards partners by ensuring they receive credit for leads they generate. This prevents conflicts over sales opportunities and strengthens trust between businesses and their partners.
- Training Access: Providing partners with access to training and educational resources equips them with the knowledge needed to sell more effectively. Training can include product knowledge, industry insights, or sales techniques, ensuring partners stay well-informed and competitive.
- Exclusive Product Access: Early access to new products or beta versions allows select partners to gain a competitive edge in the market. This incentive fosters a sense of exclusivity and deepens commitment by making partners integral to product launches and market penetration strategies.
- Public Recognition & Awards: Recognizing top-performing partners through awards, public mentions, or special designations enhances their credibility and strengthens relationships. These incentives go beyond financial rewards, providing social validation that can drive long-term loyalty.
- Advisory Council Participation: Engaging partners in strategic discussions through advisory councils fosters collaboration and ensures their perspectives are considered in decision-making processes. This involvement strengthens relationships and aligns business strategies with partner needs.
Marketing & Sales Support Incentives
- Co-Marketing Resources: Providing partners with branding materials, content, and promotional assets enables them to market products effectively. Co-marketing strategies align messaging and amplify brand visibility across multiple channels.
- Market Development Funds (MDFs): MDFs allocate financial resources to partners for marketing initiatives, helping them fund campaigns, trade show participation, or digital advertising efforts. These funds ensure partners can actively promote products while maintaining brand consistency.
- Lead Sharing: Sharing high-quality leads with strong-performing partners strengthens collaboration and ensures sales efforts are directed toward the right opportunities. This approach enhances efficiency and optimizes conversion rates.
- Joint Marketing Campaigns: Collaborative marketing campaigns align efforts between businesses and partners to maximize promotional impact. By jointly investing in marketing strategies, both parties benefit from increased reach, brand awareness, and customer engagement.
Building an Effective Partner Incentive Program
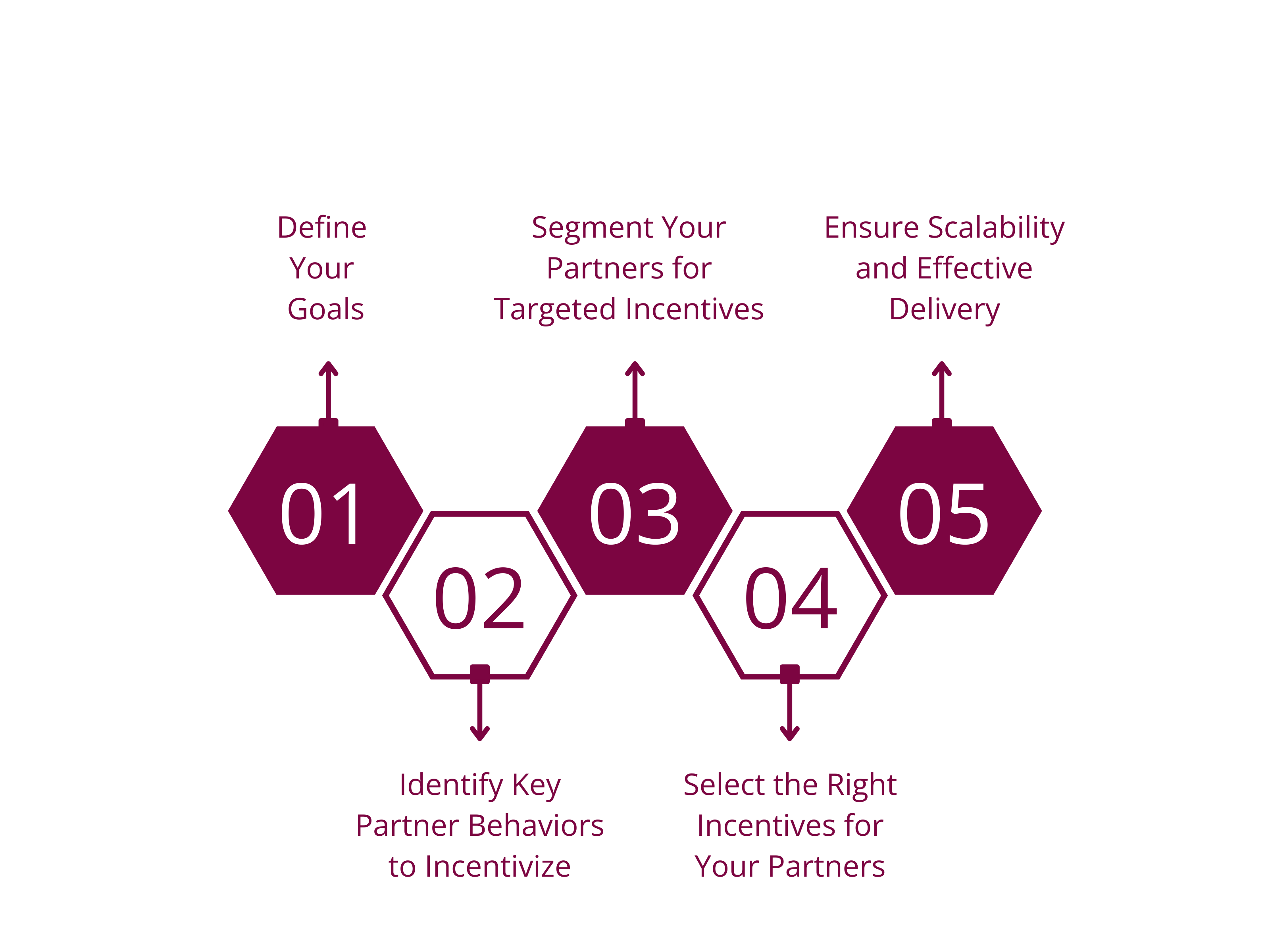
Step 1: Define Your Goals
A successful partner incentive program begins with clear objectives that align with both company goals and partner expectations. Incentives should be structured to drive measurable results, such as increased sales, higher engagement in marketing initiatives, or stronger commitment to training programs. Striking the right balance between short-term revenue growth and long-term loyalty is essential. Overemphasizing immediate sales can lead to transactional relationships, whereas a focus on engagement and skill development strengthens long-term partnerships.
Step 2: Identify Key Partner Behaviors to Incentivize
Clearly defining the behaviors that will lead to success is crucial. These can include:
- Consistent Sales Performance – Rewarding partners who meet or exceed sales targets helps maintain steady revenue flow.
- Marketing Participation – Encouraging partners to actively engage in marketing efforts, such as co-branded campaigns and lead generation activities, enhances brand visibility.
- Training and Development – Incentivizing partners to complete training programs ensures they are well-equipped to sell and support the products effectively.
- Customer Feedback Collection – Encouraging partners to gather insights from customers provides valuable data for product improvements and customer retention strategies.
A well-defined incentive structure tied to these behaviors ensures partners stay engaged and aligned with business goals.
Step 3: Segment Your Partners for Targeted Incentives
Not all partners are motivated by the same incentives. Understanding the specific roles within a partner organization allows for more tailored rewards:
- Sales Reps – Primarily driven by financial incentives such as commissions, bonuses, or lead-sharing opportunities.
- Marketing Managers – More likely to be motivated by co-marketing resources, MDFs, and brand exposure.
- Technical Teams – Often value training, exclusive product access, and participation in advisory councils.
By recognizing these differences, companies can offer incentives that resonate with each segment, leading to stronger partnerships and better performance.
Step 4: Select the Right Incentives for Your Partners
Choosing incentives requires a balance between financial and non-financial rewards while considering the short- and long-term impact.
- Financial vs. Non-Financial Incentives – While commissions and rebates provide immediate motivation, access to training, exclusive events, and deal protection can drive sustained engagement.
- Customization – The most effective programs tailor incentives to partner needs. A cybersecurity firm might prioritize technical support and market development funds, while a manufacturing business may focus on volume-based rebates.
- Balancing Short-Term vs. Long-Term Rewards – Offering a mix of immediate financial incentives and long-term benefits, such as exclusive partnerships or advisory roles, ensures partners remain committed beyond individual transactions.
Step 5: Ensure Scalability and Effective Delivery
An incentive program must be easy to manage and accessible to all partners. This requires:
- A Seamless Rewards System – The process for earning and redeeming incentives should be straightforward, with clear tracking and transparent communication.
- Technology Integration – Automation tools help manage incentives at scale, reducing administrative burden and ensuring timely payouts.
- Simplified Redemption & Payouts – Partners should be able to access their rewards without unnecessary complexity, improving overall satisfaction and participation rates.
A well-structured, scalable program that aligns with business goals and partner motivations ensures sustainable success and long-term engagement.
Common Challenges and How to Overcome Them

Lack of Partner Engagement – Making Incentives Attractive and Achievable
A major challenge in incentive programs is partners not actively participating. Often, this stems from incentives that do not align with their priorities or feel unattainable. To address this, companies must ensure rewards are relevant, easy to understand, and realistically achievable. Offering a mix of financial and non-financial incentives based on partner roles enhances participation. Regular communication about available incentives, along with simple qualification criteria, keeps partners motivated and engaged.
Complexity in Program Management – Streamlining with Rebate Management Platforms
Managing incentives across a broad partner network can become overwhelming, especially when multiple tiers, conditions, and payout structures are involved. A structured approach using rebate management platforms helps automate incentive distribution, ensuring accurate and timely payouts. These platforms track partner activity, reducing administrative overhead and minimizing errors. By integrating technology, companies can provide a seamless experience, allowing partners to focus on driving sales rather than navigating complicated reward systems.
Misalignment with Partner Needs – Regularly Gathering Feedback and Adjusting Incentives
Incentives that do not resonate with partners lead to poor participation. A common mistake is assuming all partners are driven by the same rewards. To prevent misalignment, companies must gather regular feedback through surveys, direct conversations, or advisory councils. This input ensures incentive structures reflect what partners value most, whether financial rewards, co-marketing opportunities, or exclusive product access. Adjusting incentives based on real partner insights increases engagement and ensures long-term success.
Budget Constraints – Balancing Cost-Effectiveness with Impact
Maintaining an incentive program within budget while ensuring it remains attractive can be challenging. The key is prioritizing incentives that offer high perceived value without excessive costs. Non-financial rewards, such as training access, public recognition, or strategic collaborations, can provide strong motivation without significant financial investment. Structuring incentives around performance thresholds ensures resources are allocated efficiently, rewarding high-impact contributions rather than distributing benefits too broadly.
Difficulty in Tracking Performance – Using Analytics and Reporting Tools
Without clear performance tracking, companies struggle to measure the success of their incentive programs. Many businesses face issues where incentives do not directly lead to increased sales or engagement. Implementing analytics and reporting tools allows companies to monitor key metrics, such as partner participation rates, revenue impact, and incentive utilization. Clear data insights help refine the program, ensuring rewards drive desired behaviors while maintaining transparency for partners.
Technology & Tools for Managing Partner Incentives
Rebate Management Platforms – Streamlining Incentive Tracking and Payouts
Administering partner incentives manually can lead to inefficiencies, delays, and errors. Rebate management platforms simplify the process by automating tracking, calculations, and payouts. These platforms ensure partners receive timely rewards based on predefined criteria while reducing administrative burdens. They also help companies structure volume-based rebates, loyalty-driven rewards, and performance-based bonuses with transparency, making it easier to align incentives with business objectives.
CRM & Partner Relationship Management (PRM) Systems – Centralizing Partner Data
Managing partner relationships effectively requires a centralized system to track interactions, incentives, and performance. CRM and PRM platforms store essential partner data, including sales activity, engagement levels, and incentive utilization. These tools streamline communication, making it easier to monitor partner progress, identify high-performing participants, and tailor incentives accordingly. By integrating incentive programs with PRM systems, businesses can ensure seamless coordination and better decision-making.
Real-Time Data & Analytics – Improving Transparency and Collaboration
Tracking the impact of incentives in real time provides clarity on program effectiveness. Real-time analytics tools enable businesses to measure key metrics such as partner participation, revenue growth, and return on incentive investments. This visibility helps companies refine their incentive strategies by identifying which rewards drive engagement and which need adjustment. Real-time reporting also fosters trust, as partners can access clear insights into their performance and earnings.
Automation & AI in Partner Incentives – Enhancing Efficiency
AI and automation reduce the complexity of managing large-scale incentive programs. Automated workflows eliminate manual processes, ensuring incentives are awarded based on accurate data without delays. AI-driven insights help predict partner behavior, enabling companies to personalize rewards based on past performance and preferences. Additionally, AI-powered recommendation engines suggest the most impactful incentives, ensuring resources are allocated effectively while maximizing partner engagement.
Future Trends in Partner Incentives
The Rise of Performance-Based Rewards Over Traditional Commissions
While commissions remain a standard incentive, they are becoming less influential in driving partner engagement. Many companies now recognize that performance-based rewards—such as bonuses for exceeding sales targets, exclusive benefits for consistent engagement, or tiered rewards based on long-term contributions—offer stronger motivation. These incentives ensure that partners are rewarded not just for transactions but for sustained efforts that align with business goals.
Increased Focus on Co-Marketing and MDFs for Strategic Growth
Co-marketing initiatives and Market Development Funds (MDFs) are gaining traction as businesses seek to strengthen partnerships beyond simple financial incentives. Providing funds for joint marketing efforts, lead-generation campaigns, and brand-building activities allows partners to extend their reach while driving mutual growth. However, effectively managing MDFs requires clear guidelines and performance tracking to ensure resources are allocated strategically.
The Impact of AI and Automation in Incentive Management
AI and automation are reshaping how partner incentives are structured and executed. Predictive analytics help companies design targeted rewards based on past performance and engagement patterns. Automation streamlines program administration, ensuring accurate tracking and seamless payouts. AI-driven insights also enable businesses to refine their incentive structures continuously, optimizing rewards based on real-time data and market dynamics.
Expansion of Non-Financial Incentives to Drive Partner Engagement
Non-monetary incentives are becoming a crucial component of partner programs, offering value beyond direct financial rewards. Access to early product releases, exclusive training, advisory roles, and public recognition fosters deeper relationships and long-term loyalty. As partners increasingly prioritize strategic collaboration over one-time payouts, companies are integrating more non-financial benefits to sustain engagement and commitment.
Conclusion
A well-designed partner incentive program can be a powerful driver of growth, engagement, and long-term collaboration. The key lies in understanding partner motivations, selecting the right mix of financial and non-financial rewards, and ensuring seamless program execution. As the partnership environment continues to shift toward performance-based rewards, co-marketing initiatives, and AI-driven automation, businesses must stay agile and continuously refine their approach. By prioritizing partner success and aligning incentives with shared business goals, companies can build stronger, more mutually beneficial relationships that drive sustainable results.
