What are Grocery Rebates?

Grocery rebates are a vital part of how financial incentives are structured and exchanged within the grocery supply chain. Unlike general rebate programs, which may apply to a wide range of industries and consumer products, grocery rebates involve specific agreements between suppliers, distributors, retailers, and sometimes consumers, each with defined terms, thresholds, and payout methods. These programs are not just about discounts; they are structured financial tools used to influence purchasing decisions, manage stock, and support promotional activities in a highly competitive market. Understanding how grocery rebate programs are built, tracked, settled, and optimized is essential for anyone involved in grocery procurement, distribution, or retail operations.
Table of Contents:
- What are Grocery Rebates?
- Types of Grocery Rebates
- Mechanisms of Grocery Rebate Programs
- Benefits of Participating in Grocery Rebate Programs
- Role of Rebate Management Software
Jump to a section that interests you, or keep reading.
What are Grocery Rebates?
Grocery rebates are financial incentives provided within the grocery industry to influence purchasing behaviors and enhance sales. These incentives can be directed towards various participants in the supply chain, including retailers, distributors, and consumers. The primary aim is to encourage specific actions such as bulk purchasing, promotion of particular products, or increased consumer spending.
Types of Grocery Rebates
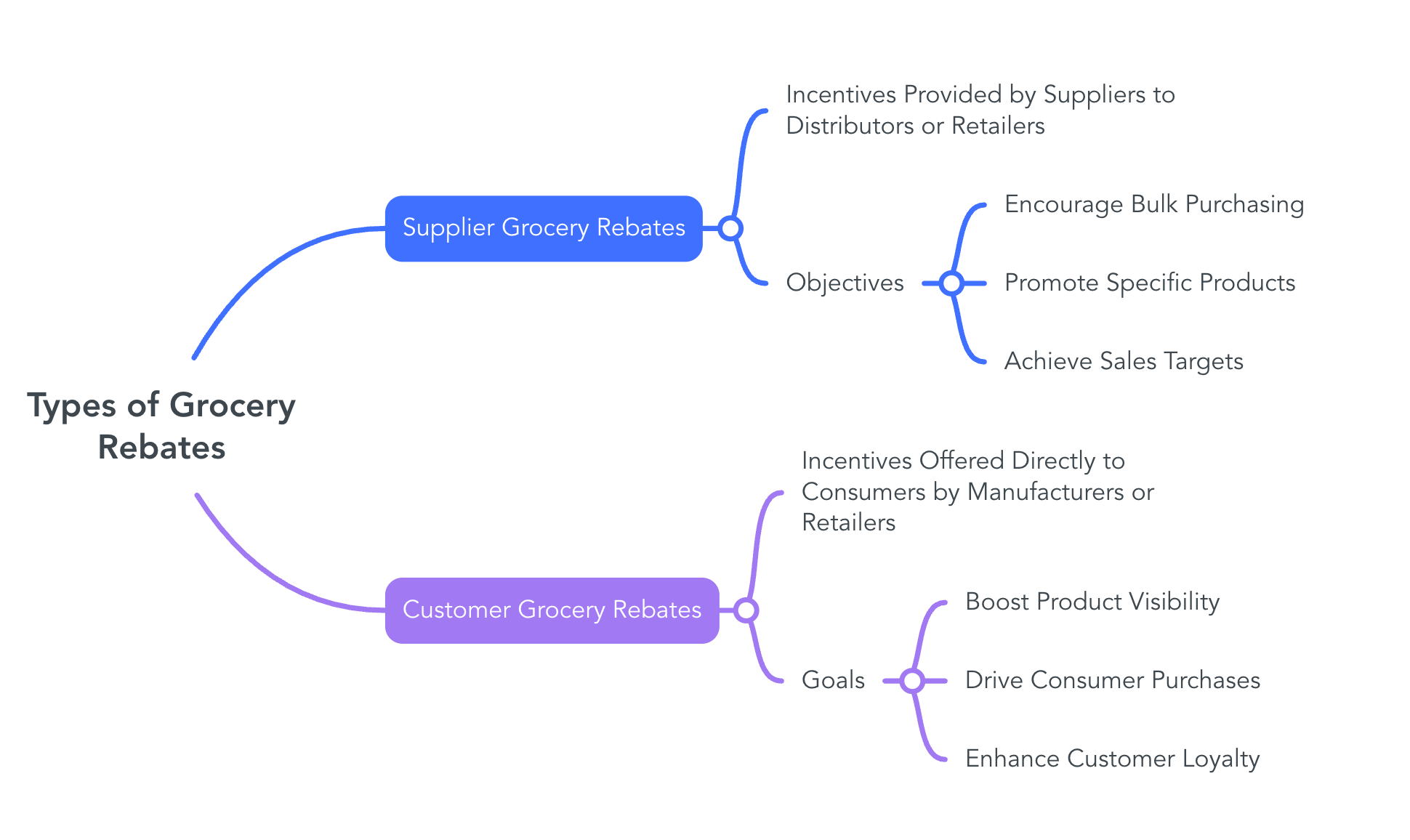
In the grocery industry, rebates are strategic financial incentives designed to influence purchasing behaviors, manage inventory levels, and support promotional activities. These rebates are primarily categorized into two types: Supplier Grocery Rebates and Customer Grocery Rebates.
Supplier Grocery Rebates
-
Incentives Provided by Suppliers to Distributors or Retailers
Supplier grocery rebates are retrospective financial incentives offered by manufacturers or producers to grocery distributors or retailers. These rebates are typically contingent upon the distributor or retailer meeting specific conditions outlined in a rebate agreement. Such conditions may include purchasing a certain volume of products, achieving growth targets, or promoting particular items. Upon fulfillment of these conditions, the supplier provides a rebate, effectively reducing the cost of goods sold for the distributor or retailer.
-
Objectives
-
Encourage Bulk Purchasing: By offering rebates tied to volume thresholds, suppliers motivate distributors and retailers to increase their order quantities. This strategy helps suppliers achieve higher sales volumes and economies of scale.
-
Promote Specific Products: Suppliers may introduce rebates for particular products to boost their market presence. Retailers, incentivized by these rebates, are more likely to prioritize shelf space and marketing efforts for these items, leading to increased consumer awareness and sales.
-
Achieve Sales Targets: Rebates can be structured to reward retailers or distributors for meeting or exceeding predetermined sales goals. This not only drives higher sales but also fosters a collaborative relationship between suppliers and retailers, aligning their objectives for mutual benefit.
-
Customer Grocery Rebates
-
Incentives Offered Directly to Consumers by Manufacturers or Retailers
Customer grocery rebates are financial incentives provided directly to end consumers by manufacturers or retailers. Unlike supplier rebates, which are business-to-business, these rebates are consumer-focused and aim to influence purchasing decisions at the individual level. Typically, consumers pay the full price at the point of sale and later receive a portion of the purchase price back after submitting proof of purchase and meeting any additional requirements.
-
Goals
-
Boost Product Visibility: By offering rebates, manufacturers and retailers can draw attention to specific products. The prospect of a partial refund can make products stand out on crowded shelves, encouraging consumers to choose them over competing items.
-
Drive Consumer Purchases: Financial incentives in the form of rebates can make products more appealing, especially to price-sensitive shoppers. This can lead to increased sales volumes and help in clearing out inventory, particularly for new or seasonal products.
-
Enhance Customer Loyalty: Successfully redeemed rebates can lead to positive consumer experiences, fostering trust and encouraging repeat purchases. When customers feel they are receiving value through rebates, they may develop a preference for the brand or retailer, leading to long-term loyalty.
-
Mechanisms of Grocery Rebate Programs

Grocery rebate programs are structured systems designed to offer financial incentives that promote specific purchasing behaviors within the grocery industry. The successful implementation of these programs involves several critical stages: establishing agreements, tracking purchases, calculating rebates, and issuing payments.
Establishing Agreements
-
Negotiation of Terms Between Involved Parties
The initiation of a grocery rebate program begins with a formal agreement between suppliers (manufacturers or producers) and buyers (distributors or retailers). This agreement outlines the terms and conditions of the rebate program, including the duration, the specific products involved, and the responsibilities of each party. Clear documentation of these terms is essential to prevent misunderstandings and ensure smooth operation.
-
Setting Purchase Thresholds and Rebate Percentages
Within the agreement, specific targets are established that participants must meet to qualify for rebates. These targets can be based on purchase volumes, sales figures, or other performance metrics. Corresponding rebate percentages or amounts are defined, indicating the financial incentives provided upon achieving these targets. Setting realistic and attainable thresholds motivates participants to strive for them, benefiting both suppliers and buyers.
Tracking Purchases
-
Monitoring Product Purchases During the Rebate Period
Accurate tracking of purchases is vital to determine eligibility for rebates. This involves systematically recording transactions that occur within the rebate period. Utilizing automated systems or rebate management software can enhance accuracy and efficiency in tracking, reducing the risk of errors and disputes. Consistent monitoring ensures that all qualifying purchases are accounted for, facilitating fair and prompt rebate settlements.
Calculating Rebates
-
Applying Agreed-Upon Percentages to Total Purchases
At the conclusion of the rebate period, the total eligible purchases are calculated. The predetermined rebate percentages are then applied to this total to determine the rebate amount. For example, if a retailer purchases $100,000 worth of a product with a 5% rebate agreement, they would be entitled to a $5,000 rebate. Accurate calculations are crucial to ensure that participants receive the correct rebate amounts.
Issuing Rebates
-
Credit to Accounts or Direct Payments to Eligible Participants
Once the rebate amounts are calculated and verified, the funds are issued to the eligible participants. This can be done through direct payments, such as electronic funds transfers or checks, or by crediting the participant's account for future purchases. Timely and accurate issuance of rebates is essential to maintain trust and encourage continued participation in the rebate program.
Benefits of Participating in Grocery Rebate Programs
Engaging in grocery rebate programs offers several advantages for distributors, retailers, and suppliers. These benefits encompass cost reductions, sales growth, and enhanced product promotion.
Cost Reductions
-
Lowering Cost of Goods Sold for Distributors and Retailers
By meeting specific purchase volumes or sales targets outlined in rebate agreements, distributors and retailers can earn rebates that effectively reduce their cost of goods sold (COGS). This reduction allows businesses to improve their profit margins and offer more competitive pricing to consumers.
-
Potential Reinvestment into Business Growth Areas
The savings accrued from rebates can be strategically reinvested into various facets of the business, such as marketing initiatives, infrastructure enhancements, or expanding product lines. This reinvestment fosters overall business growth and strengthens market positioning.
Sales Growth
-
Motivating Increased Purchase Volumes
Rebate programs are structured to incentivize higher purchase volumes by setting thresholds that, when met, qualify participants for financial rewards. This motivation encourages distributors and retailers to increase their order quantities, leading to elevated sales figures.
-
Implementing Promotional Strategies to Meet Rebate Criteria
To achieve the targets necessary for rebates, businesses often adopt aggressive promotional strategies, including discounts, bundling offers, and in-store promotions. These tactics not only help in meeting rebate criteria but also attract more customers, thereby boosting sales.
Product Promotion
-
Linking Rebates to Promotional Activities
Suppliers frequently tie rebate offers to specific promotional activities, such as in-store displays, advertising campaigns, or special events. By participating in these activities, retailers can enhance product visibility and appeal. citeturn0search0
-
Enhancing Brand Recognition and Customer Loyalty
Effective promotion through rebate-linked activities increases brand recognition and fosters customer loyalty. Consumers become more familiar with and trusting of brands that are consistently promoted and associated with value-added offers, leading to repeat purchases and long-term customer relationships.
Role of Rebate Management Software
In the grocery industry, managing rebate programs can be complex and time-consuming. Rebate management software plays a crucial role in automating and streamlining these processes, enhancing accuracy, efficiency, and visibility.
Automation and Streamlining of Rebate Processes
-
Reduction of Administrative Workload Through Automated Calculations
Traditional rebate management often involves manual calculations, which are prone to errors and require significant administrative effort. Rebate management software automates these calculations, ensuring accuracy and reducing the time spent on administrative tasks. This automation minimizes human error and accelerates the processing of rebates.
-
Simplification of Processes from Agreement Setup to Final Payout
From establishing rebate agreements to issuing final payouts, rebate management software streamlines each step. It provides a centralized platform where all rebate-related activities can be managed efficiently, reducing complexities and ensuring that all parties adhere to the agreed-upon terms. This simplification leads to faster turnaround times and improved compliance with rebate agreements.
Enhanced Visibility and Reporting
-
Centralized Storage of Rebate Deals for Granular Analysis
Rebate management software offers centralized storage for all rebate agreements and related data. This centralization allows for detailed analysis of each deal, enabling businesses to assess performance, identify trends, and make informed decisions. Having all data in one place facilitates better tracking and management of rebate programs.
-
Real-Time Tracking and Reporting Capabilities for Monitoring Progress Toward Rebate Thresholds
With real-time tracking and reporting features, rebate management software enables businesses to monitor their progress toward achieving rebate thresholds continuously. This immediate visibility helps in making timely adjustments to purchasing strategies to maximize rebate earnings. Real-time insights also aid in forecasting and planning future activities related to rebate programs.
Conclusion
Grocery rebate programs are more than short-term financial incentives; they’re structured agreements that help suppliers, distributors, and retailers align their goals, manage costs, and promote targeted products. When these programs are clearly negotiated, accurately tracked, and efficiently settled, they become a dependable source of financial advantage and operational clarity. With the support of rebate management software, businesses in the grocery sector can avoid manual errors, gain real-time visibility, and manage complex rebate arrangements with more confidence. As margins tighten and competition increases, having a well-run rebate system is not just helpful, it’s necessary for maintaining consistency and control in everyday grocery operations.
